As the demand for faster and more reliable wireless connectivity continues to grow, the development of new Wi-Fi standards becomes essential. Wi-Fi 8, the upcoming iteration in wireless networking, promises to revolutionize how we connect to the internet. In this article, we’ll delve into what Wi-Fi 8 is, explore its key features—including Coordinated Spatial Reuse (Co-SR)—and look at the anticipated timeline for its rollout.
Table of Contents
What is Wi-Fi 8?
Wi-Fi 8 refers to the next generation of wireless networking standards currently under development, anticipated to be standardized as IEEE 802.11bn. Building upon the advancements of Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be), Wi-Fi 8 aims to deliver unprecedented data speeds, lower latency, and enhanced spectrum efficiency. These improvements are crucial for supporting emerging technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Key Features of Wi-Fi 8
Coordinated Spatial Reuse (Co-SR)
A standout feature expected in Wi-Fi 8 is Coordinated Spatial Reuse (Co-SR). Co-SR enhances spectrum efficiency by allowing multiple devices to transmit simultaneously on the same frequency band without causing significant interference. This is achieved through advanced coordination protocols between access points (APs) and client devices, optimizing the use of available spectrum and increasing network capacity.

How Co-SR Works
- Network Coordination Setup: APs establish a coordination protocol, sharing information about their transmission schedules and capabilities.
- Channel Information Exchange: APs and devices exchange channel state information, detailing signal strength and interference levels.
- Transmission Parameter Negotiation: Devices negotiate parameters like power levels and modulation schemes to minimize interference.
- Dynamic Resource Allocation: The network allocates spectrum resources dynamically, allowing simultaneous transmissions.
- Concurrent Transmission Execution: Multiple devices transmit concurrently, using advanced signal processing to mitigate interference.
- Feedback and Adaptation: Devices provide real-time feedback, enabling the network to optimize transmission parameters continually.
Higher Data Rates and Lower Latency
Wi-Fi 8 aims to push wireless speeds to new heights, potentially exceeding the multi-gigabit speeds of Wi-Fi 7. By utilizing advanced modulation schemes and wider channel bandwidths, users can expect significantly higher data rates and reduced latency. This is essential for applications that require real-time data transmission, such as online gaming and streaming ultra-high-definition video content.
Enhanced Spectrum Efficiency
With the integration of Co-SR and other advanced technologies, Wi-Fi 8 will make better use of the available spectrum. This means more devices can connect simultaneously without a drop in performance, addressing the challenges posed by the growing number of connected devices in homes and businesses.
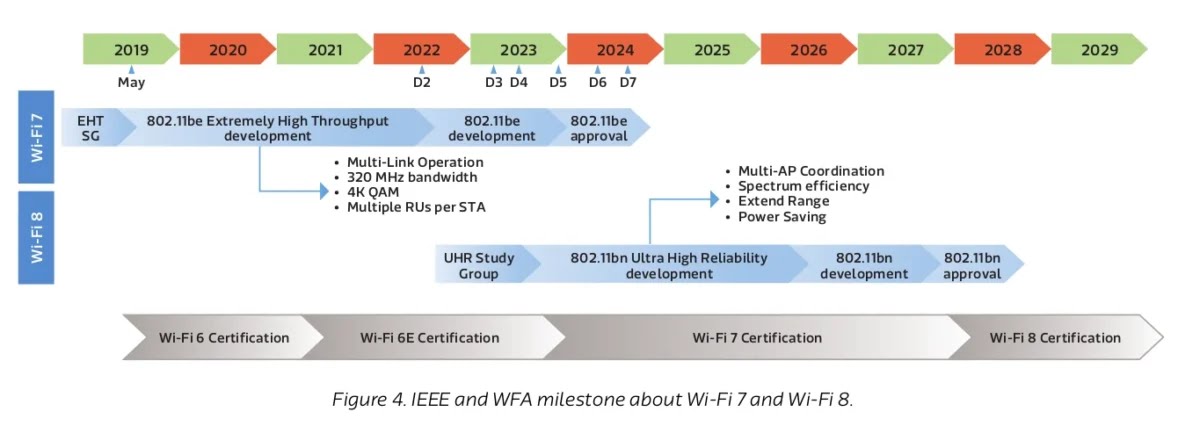
Wi-Fi 8 Timeline
The development and rollout of Wi-Fi 8 are projected as follows:
- 2024-2025: Draft specifications for IEEE 802.11bn are developed and released for industry review.
- 2026-2027: Early adoption begins, with companies developing Wi-Fi 8-compatible hardware based on draft standards.
- 2028: Official approval of the IEEE 802.11bn standard.
- 2029 and Beyond: Widespread deployment of Wi-Fi 8 devices and networks.
This timeline indicates that while official standardization is a few years away, the industry is expected to proactively develop and test Wi-Fi 8 technologies ahead of time.

Early Implementations and Industry Adoption
Historically, companies have introduced hardware based on draft specifications before the official standardization of new Wi-Fi versions. For instance, with Wi-Fi 7, companies like MaxLinear introduced the MxL31712/MxL31708 chips, and Qualcomm launched the Networking Pro Series Gen 3 in 2022. Similarly, we may see early Wi-Fi 8 implementations as soon as 2026 or 2027.
What Wi-Fi 8 Means for Consumers and Businesses
Improved Connectivity in Dense Environments
Wi-Fi 8’s advanced features will significantly improve performance in environments with a high density of devices, such as airports, stadiums, and office buildings. Co-SR and enhanced spectrum efficiency ensure reliable connectivity even when many devices are competing for bandwidth.

Support for Advanced Applications
The higher data rates and lower latency of Wi-Fi 8 make it ideal for supporting advanced applications that require real-time data transmission. This includes:
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Seamless experiences without lag or buffering.
- Real-Time Gaming: Smoother gameplay with minimal latency.
- 8K and Ultra-HD Streaming: Flawless streaming of high-definition content.
Future-Proofing Networks
Adopting Wi-Fi 8 will help future-proof networks, ensuring they can handle the increasing demands of new technologies and the growing number of connected devices in the IoT ecosystem.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi 8 represents a significant leap forward in wireless networking technology. With features like Coordinated Spatial Reuse (Co-SR), higher data rates, and improved spectrum efficiency, it is poised to meet the connectivity demands of the future. As development progresses and more information becomes available, staying informed about Wi-Fi 8 will help consumers and businesses prepare for the next era of wireless communication.
This article is part of an ongoing series exploring advancements in wireless technology. Stay tuned for more updates on Wi-Fi 8 and other emerging technologies.