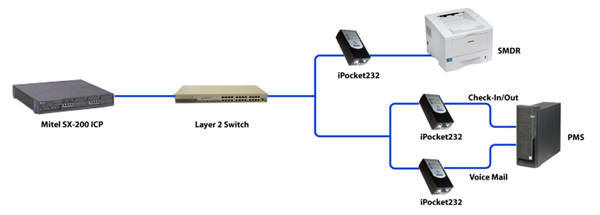
In a hospitality environment, integrating the Property Management System (PMS) with the Mitel SX-200 system is essential for automating guest services like check-in, check-out, voicemail management, and call billing. A key component in this integration is the serial transceiver, which converts serial data from the PMS into TCP/IP packets for transmission over the network to the Mitel SX-200 PBX.
1. Overview of PMS Integration with Mitel SX-200
The PMS in a hotel typically manages a variety of guest services, including room status, billing, and guest messaging. To facilitate this, the PMS system needs to communicate with the hotel’s telephony system—in this case, the Mitel SX-200.
Key Components in the Integration:
- Mitel SX-200 ICP: The central hub for managing telephony services, including guest room phones and voicemail.
- PMS Server: The system that handles guest-related services, typically provided by a third-party PMS vendor.
- Serial Interface: The PMS often communicates via a serial interface, which is not directly compatible with modern networked systems.
- Serial Transceiver (iPocket232): Converts the serial signals from the PMS into TCP/IP packets, allowing them to be transmitted over the network to the SX-200.
2. How the Integration Works
Serial to TCP/IP Conversion:
- The PMS server sends guest-related data (e.g., check-in/check-out commands, room status updates) through a serial interface.
- This data is transmitted via a serial cable to the serial transceiver (e.g., iPocket232). The transceiver then converts these serial signals into TCP/IP packets.
- The TCP/IP packets are sent over the hotel’s network (usually through a Layer 2 switch) to the Mitel SX-200 system.
Mitel SX-200 Processing:
- The SX-200 receives these packets via a designated TCP port and processes the commands to update its internal settings, such as enabling a room phone for external calls or activating a voicemail box.
3. Detailed Component Functions
PMS Server:
- Function: The PMS server manages hotel operations related to guest services. It generates and sends serial commands that need to be processed by the telephony system.
- Output: Serial data that includes instructions like guest check-in or checkout, which needs to be communicated to the Mitel SX-200.
Serial Transceiver (iPocket232):
- Function: Acts as a bridge between the serial communication of the PMS and the TCP/IP-based network of the hotel.
- Operation: The transceiver converts serial data from the PMS into TCP/IP packets. It is connected to the network switch, which forwards the data to the Mitel SX-200.
Mitel SX-200 ICP:
- Function: The PBX system processes the TCP/IP packets received from the network and executes commands accordingly. This might include enabling room phones, activating message waiting lights, or routing billing information.
- Input: TCP/IP packets containing PMS commands.
4. The Importance of Network Configuration
The network plays a crucial role in ensuring that the PMS integration functions smoothly:
- Layer 2 Switch: Facilitates the communication between the PMS server (via the serial transceiver) and the Mitel SX-200 system. Proper VLAN configuration may be necessary to prioritize PMS-related traffic, ensuring that commands are processed without delay.
- TCP Ports: The SX-200 is configured to listen on specific TCP ports (as programmed in the PBX system settings) to receive PMS commands. It is critical that these ports are correctly set up in both the transceiver and the SX-200 to avoid communication failures.
5. Testing and Troubleshooting
To ensure that the PMS and SX-200 integration is functioning correctly:
- Testing:
- Verify that commands from the PMS are reaching the SX-200 by initiating a check-in or check-out operation. Ensure that the corresponding actions (e.g., enabling room phone or activating voicemail) are performed correctly.
- Use network tools to test the connectivity between the serial transceiver and the SX-200.
- Troubleshooting:
- Connection Issues: Ensure that the serial cable is securely connected to the transceiver and that the transceiver is properly configured to communicate with the network.
- Network Problems: Verify that the Layer 2 switch is correctly forwarding traffic to the SX-200. Check for any network issues that might be blocking or delaying TCP/IP packets.
Conclusion
The integration of a PMS with a Mitel SX-200 system relies heavily on the effective conversion of serial data to TCP/IP packets using a serial transceiver. By understanding the roles of each component—PMS server, serial transceiver, Layer 2 switch, and the Mitel SX-200—you can ensure a smooth and efficient setup that enhances guest services and hotel operations. Proper configuration and regular testing are key to maintaining a reliable connection between these systems.