Troubleshooting, adoption, and maintenance via command line
Table of Contents
Accessing UniFi devices via SSH is one of the most powerful ways to troubleshoot issues, inspect device settings, adopt devices manually, or perform advanced configuration and reset tasks. This guide walks you through how to SSH into a UniFi device and lists the most useful SSH commands with explanations.
What is SSH?
SSH (Secure Shell) provides secure remote command-line access to UniFi access points, switches, gateways, and other devices. SSH is especially useful when devices are:
- Offline or stuck in a provisioning state
- Failing to adopt into a UniFi Network application
- Experiencing unknown configuration or performance issues
How to SSH into a UniFi Device
You can SSH into UniFi devices in two ways:
1. From your computer
- macOS/Linux: Open the Terminal app and use the
sshcommand - Windows: Use Windows Terminal (built-in) or install PuTTY
Command format:
ssh username@ip_address
Example:
ssh [email protected]
2. From the UniFi Controller’s Debug Terminal
The UniFi Controller provides a browser-based SSH session under Settings → System → Debug Terminal, though this is less flexible.
Default UniFi SSH Credentials
The login varies by firmware and model:
| Device Type | Default Username | Default Password |
|---|---|---|
| UniFi AP (old FW) | ubnt | ubnt |
| UXG Gateway | root | ubnt |
| New devices | ui | ui |
If the device is already adopted, the SSH credentials are site-specific. To find them:
- Go to Settings → System → Advanced → Device Authentication
Each site may have different randomized SSH credentials.
Common UniFi SSH Commands
Here’s a breakdown of the most used and helpful SSH commands for UniFi:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
info | Displays the device status, model, firmware, and inform URL |
set-inform http://ip:8080/inform | Manually point the device to a UniFi Controller |
uptime | Shows how long the device has been running |
reboot | Restarts the device |
help | Lists all available commands for the device |
syswrapper.sh restore-default or set-default | Factory resets the device |
cat /etc/hostname | Displays the hostname of the device |
ls / ls -la | Lists directory contents (basic navigation) |
top | Shows running processes and CPU/memory usage |
free -m | Displays memory usage in MB |
df -h | Displays disk space usage |
ifconfig or ip a | Lists network interfaces and IPs |
ping 8.8.8.8 | Tests basic internet connectivity |
logread | Displays system log (may vary by model) |
cat /tmp/system.cfg | Shows system configuration on some UniFi devices |
tail -f /var/log/messages | Follows live logs for debugging |
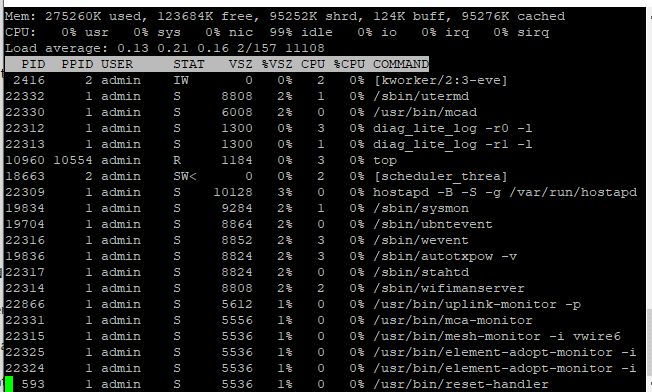
Real-World Example: Process List on a UniFi AP
Using the top command on a UniFi AP reveals running processes like:
bashCopyEdit/usr/sbin/ubnt-discover
/usr/sbin/hostapd
/sbin/sysmon
/usr/bin/element-monitor
/usr/bin/reset-handler
These processes help manage wireless services, system events, provisioning, and inform communication.
Pro Tips
- Always check the
infocommand first to confirm the inform URL and adoption status. - Use
set-informif you’re adopting a device manually to a local or cloud-based controller. - Don’t interrupt firmware updates. Use
uptimeandtopto monitor device status before resetting. - Use
rebootorsyswrapper.sh restore-defaultcarefully, especially on remote deployments.
Final Thoughts
SSH is an indispensable tool for any network admin working with UniFi gear. Whether you’re dealing with stubborn provisioning issues or just want to monitor performance, these commands give you fast access to the data and tools you need.